AS/AD MODEL
THE AS/AD MODEL
The AS/AD model shows that the equilibrium of AS and AD determines the current output (real GDP) and the price level.
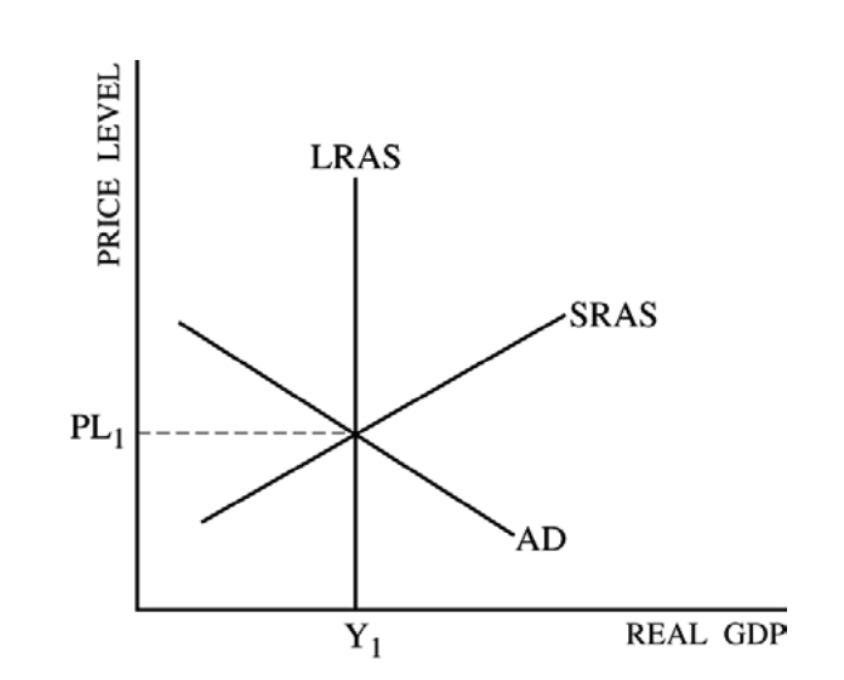
Full employment equilibrium exists where AD intersects SRAS and LRAS at the same point.
Full employment equilibrium exists where AD intersects SRAS and LRAS at the same point.

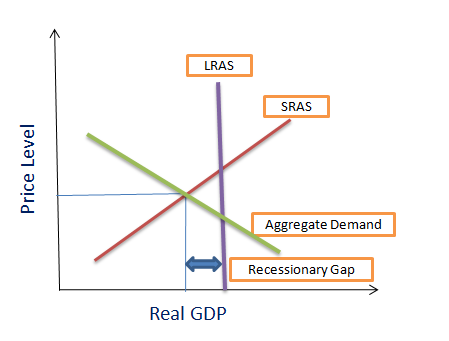
An inflationary gap exists when equilibrium occurs beyond full employment output.
The three ranges of SRAS:
- keynesian or horizontal range
- intermediate range
- classical or vertical range
keynesian or horizontal range happens when there recession or depression, when resources are not being fully used, or when we're below full employment
intermediate-range happens when resources are getting closer to full employment levels, which creates upward pressure on wages and prices
classical or vertical range happens when real GDP is at a level below the full employment level and any increase in demand will result only in an increase in prices
demand-pull inflation is an increase in the average price level resulting from an increase in total spending in the economy. C, I, G, and X make the AD in a nation. AD always increases.
cost-push inflation is when firms respond to rising costs by increasing their prices to protect profit margins. It can be caused by...:
- rising unit labor costs
- an increase in the price of raw materials
- a depreciation in the exchange rate causing a rise in import costs
- an increase in business taxes,
- expectations in the inflation rate
Some factors that affect inflationary pressures are...:
- rising property prices -> increased consumer wealth -> demand-pull inflation risk
- increasing world oil prices -> higher costs for businesses -> cost-push inflation risk
- depreciating exchange rate -> increased import prices and rising exports -> cost-push and demand-pull inflation risk
- the rapid expansion of money and credit from banks -> rising consumer spending financed by loans -> demand-pull inflation risk
If you still don't understand, here are some vids 2 help :) :
Short-run and long-run equilibrium and the business cycle: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/ap-macroeconomics/national-income-and-price-determinations/equilibrium-in-the-ad-as-model-ap/v/short-run-and-long-run-equilibrium-and-the-business-cycle-ap-macroeconomics-khan-academy?modal=1
Demand-pull inflation: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/ap-macroeconomics/national-income-and-price-determinations/changes-in-the-ad-as-model-in-the-short-run-ap/v/demand-pull-inflation-under-johnson?modal=1
Cost-push inflation: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/ap-macroeconomics/national-income-and-price-determinations/changes-in-the-ad-as-model-in-the-short-run-ap/v/cost-push-inflation?modal=1

Comments
Post a Comment