AGGREGATE SUPPLY
AGGREGATE SUPPLY
Aggregate supply (AS) is the level of real GDP that firms will produce at each price level
Long-run is the period of time where input prices are completely flexible and adjust to changes in the price level. In the long-run, the level of real GDP supplied is independent of the price level.
Short-run is the period of time where input prices are sticky and don't adjust to changes in the price level. In the short-run, the level of real GDP supplied is directly related to the price level.
The two types of aggregate supply are:
- long-run aggregate supply (LRAS)
- short-run aggregate supply (SRAS).
Long-run aggregate supply marks the level of full employment in the economy. Because input prices are completely flexible in the long-run, changes in price level don't change firms' real profits and therefore don't change firms' level of output. LRAS is vertical at the economy's level of full employment.
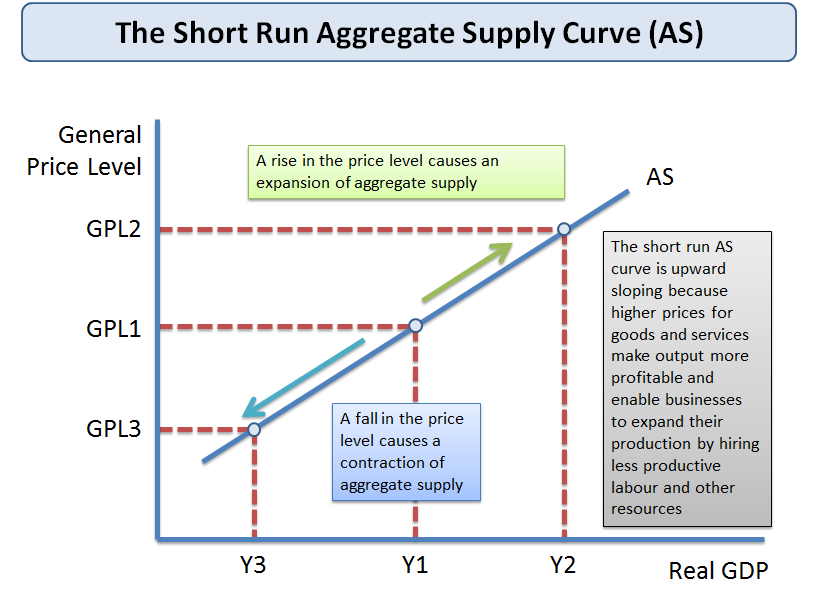
Short-run aggregate supply happens because input prices are sticky in the short-run, which means the SRAS is upward sloping.
Changes in SRAS:
- an increase in SRAS shifts to the right
- a decrease in SRAS shifts to the left
Shifts in SRAS happen because of the per-unit cost of production.
The equation is:
per unit production cost = (total input cost)/(total output)
The determinants for SRAS are:
- input or resource prices
- productivity
- legal-institutional environment.
The categories for input/resource prices are:
- domestic resource prices
- foreign resource prices
- market power
It is also important to know:
- increases in resource prices = SRAS <-
- decreases in resource prices = SRAS ->
Productivity = (total output)/(total input)
- more productivity = lower unit production cost = SRAS ->
- lower productivity = higher unit production cost = SRAS <-
The two parts of the legal-institutional environment are:
- taxes and subsidies
- taxes = SRAS <-
- subsidies = SRAS ->
- government regulation
- government regulation creates a cost of compliance = SRAS <-
- deregulation reduces compliance costs = SRAS ->
Short-run aggregate supply: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UwAQRnpVMzI
Long-run aggregate supply: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a2azB2eag5I

Comments
Post a Comment